On-page SEO (also known as on-site SEO) refers to the practice of optimizing individual web pages to make them more search engine-friendly and user-friendly. The primary goal of search engine optimization is to improve a page’s search engine ranking and increase organic traffic.
Key activities in on-page SEO include optimizing title tags, content, internal links, and URLs to align with search intent.
In this blog, we’ll explore various techniques for optimizing your website’s pages to meet on-page SEO requirements.
What is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO, also called on-site SEO, is the process of optimizing individual web pages to improve their visibility in search engine results and provide a better user experience. It involves refining both the content and the HTML source code of a page to make it more relevant, informative, and accessible to both search engines and users.
The goal of on-page SEO is to ensure your web pages rank higher for specific keywords, attract more organic traffic, and provide value to visitors by aligning with their search intent.
On-Page SEO vs Off-Page SEO

When it comes to improving your website’s visibility on search engines like Google, there are two main strategies: On-Page SEO and Off-Page SEO.
- On-page SEO refers to all the things you can do directly on your website to improve its ranking. This includes optimizing content, images, URLs, title tags, and more. The idea is to make your website easy for both search engines and users to understand.
- Off-page SEO is all about actions taken outside of your website to improve its position in search rankings. This mainly includes building backlinks from other reputable websites. When other websites link to your page, it signals to search engines that your content is valuable and trustworthy. If you’re mapping the bigger picture, this practical primer on off-page SEO for beginners helps frame how authority complements on-page work. off-page SEO for beginners.
In short, On-Page SEO focuses on what happens on your website itself, while Off-Page SEO focuses on building your website’s authority and reputation from external sources.
Why On-Page SEO is Important?
On-page SEO is crucial because it directly affects how search engines understand and rank your website. Without optimizing your web pages for search engines, even the best content might not be discovered by your target audience. Here’s why On-Page SEO is so important:
- Helps Search Engines Understand Your Content
Search engines like Google use algorithms to decide which websites should appear in search results. For these algorithms to rank your page higher, they need to understand what your page is about. On-page SEO includes elements like title tags, headers, and keywords that help search engines know the content and relevance of your webpage. When you optimize these elements, search engines can easily understand your page and show it to users who are searching for similar content. Under the hood, foundational technical SEO, crawlability, internal linking logic, page speed, and canonical signals keep those on-page elements discoverable and interpretable. What is technical SEO. - Improves User Experience (UX)
On-page SEO isn’t just about search engines. It’s also about making your website easier and more enjoyable for visitors. If your website loads fast, is easy to navigate and displays well on mobile devices, users will stay longer. This is important because search engines pay attention to how users interact with your site. A good user experience leads to more visitors, lower bounce rates, and higher chances of conversions. - Increases Organic Traffic
Proper On-Page SEO helps your pages rank higher in search engine results. When your pages Mrank well, they’re more likely to get clicked on, bringing in more organic traffic (visitors who find your site through search engines). The better optimized your pages are, the more chances you have of attracting visitors without having to pay for ads. - Helps You Target the Right Keywords
On-page SEO allows you to focus on specific keywords and search intent. This means you can optimize each page for the specific queries people are searching for. When your content aligns with the right keywords, it increases the chances of your page ranking for those searches, bringing in more targeted traffic. - Supports Content Strategy
On-page SEO helps structure your content in a way that makes it easy for both users and search engines to digest. Using headers, keywords, and proper formatting ensures your content is not only informative but also easy to read. This improves your chances of ranking for a variety of related searches and allows you to cover all aspects of a topic comprehensively. - Improves Your Website’s Authority and Credibility
When your pages are optimized, users are more likely to trust and stay on your site. They will see it as a reliable source of information, which helps improve your site’s overall authority. Plus, if people spend more time on your site and share your content, it can lead to more backlinks (other websites linking to your page), which further boosts your search engine ranking. - Increases Conversion Rates
Ultimately, On-Page SEO helps drive more visitors to your website, but it also helps convert those visitors into customers or subscribers. Optimizing elements like call-to-action buttons, forms, and page layouts makes it easier for users to take the desired actions, whether it’s buying a product, signing up for a newsletter, or contacting you.
Key Elements of On-Page SEO
1. Keyword research
Keyword research is the process of finding the words and phrases that people are searching for on search engines like Google, Yahoo, or Bing. These words, known as keywords, are what users type into the search bar when they want to find information, products, or services. A complete keyword strategy also weighs intent, difficulty, and topical coverage so your on-page work lines up with how people actually search. SEO keyword complete guide.
The goal of keyword research is to identify the best keywords to target for your website so that you can create content that matches what people are looking for. By using these keywords in your content, you can help your website rank higher on search engines and attract more visitors.
Why is Keyword Research Important?
Keyword research is essential because it helps you understand what your audience is interested in. When you know which keywords people are using, you can create content that answers their questions, solves their problems, or provides them with the information they need. This not only helps you rank higher on search engines but also increases your chances of connecting with your target audience.
For example, if you own a bakery and you do keyword research, you might discover that a lot of people are searching for “gluten-free cake recipes.” Knowing this, you can create a blog post or webpage about gluten-free cakes, and optimize it with that keyword. This helps your website show up when someone searches for that term.
Steps in Keyword Research
- Brainstorm Initial Ideas: Start by thinking about the main topics or services related to your business. These could be broad terms like “fitness,” “food,” or “gardening.”
- Use Keyword Research Tools: Tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Ubersuggest can help you find specific keywords people are searching for. These tools will show you how many people search for a keyword each month and how competitive that keyword is.
- Analyze Search Intent: It’s important to understand why people are searching for a particular keyword. Are they looking for information, or do they want to make a purchase? This is called search intent. Understanding search intent helps you create content that matches what users are actually looking for.
- Choose the Best Keywords: After finding several keyword ideas, pick the ones that are most relevant to your website and have a good balance of search volume (how many people are searching for them) and competition (how hard it is to rank for those keywords). You don’t want to target keywords that are too competitive, as it can be hard to rank for them.
- Optimize Your Content: Once you have your keywords, include them in important parts of your webpage, such as the page title, meta description, headers, and throughout the content. But remember, use them naturally. Keyword stuffing (overusing keywords) can hurt your rankings.
Types of Keywords
- Short-tail keywords: These are broad and general keywords that usually consist of one or two words, like “shoes” or “fitness.” While they have high search volume, they are also highly competitive.
- Long-tail keywords: These are longer, more specific phrases like “best-running shoes for women” or “home fitness routine for beginners.” These keywords usually have lower search volume but less competition, making them easier to rank for.
- LSI Keywords (Latent Semantic Indexing): These are related terms or synonyms that help search engines understand the context of your content. For example, if your main keyword is “fitness,” LSI keywords might be “exercise,” “workout,” or “gym.”

2. Page title
A page title is one of the most important elements in On-Page SEO. It’s the title that appears at the top of your web browser and is also displayed on search engine results pages (SERPs) when someone searches for something related to your content.
Page titles are crucial because they help both search engines and users understand what your page is about. When you create a page title, you’re essentially telling Google and visitors what to expect when they click on your page.
Why Are Page Titles Important?
- Search Engine Ranking: Google uses page titles to understand the main topic of your page and decide where to rank it in search results. A clear and relevant title with important keywords can improve your chances of ranking higher.
- User Experience: A good page title helps users quickly understand whether your page contains the information they’re looking for. If the title matches their search query, they’re more likely to click on it.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The page title is one of the first things users see in search results. If it’s engaging and relevant, users are more likely to click on it. A high CTR can also help improve your search rankings.
Key Elements of a Good Page Title
- Relevance: Your page title should reflect the content on the page accurately. If users find what they expect when they click, they are more likely to stay on your site.
- Incorporate Keywords: Use important keywords in the page title. This helps search engines understand what your page is about and increases your chances of ranking higher. But avoid keyword stuffing — make sure the title still reads naturally.
- Length: Keep your title under 60 characters. Titles that are too long get cut off in search results, making it harder for users to understand what your page is about. A shorter title is more user-friendly and more likely to appear fully in search results.
- Branding: Including your brand name at the end of the title can help with brand recognition. This is especially useful for home pages or high-traffic pages.
Example:
If you have a page about “On-Page SEO Tips,” a good page title could be:
“On-Page SEO Tips for Beginners – Boost Your Google Rankings”
This title is clear, includes relevant keywords like “On-Page SEO Tips” and “Google Rankings,” and provides value to users by mentioning that it’s for beginners.
3. Headings
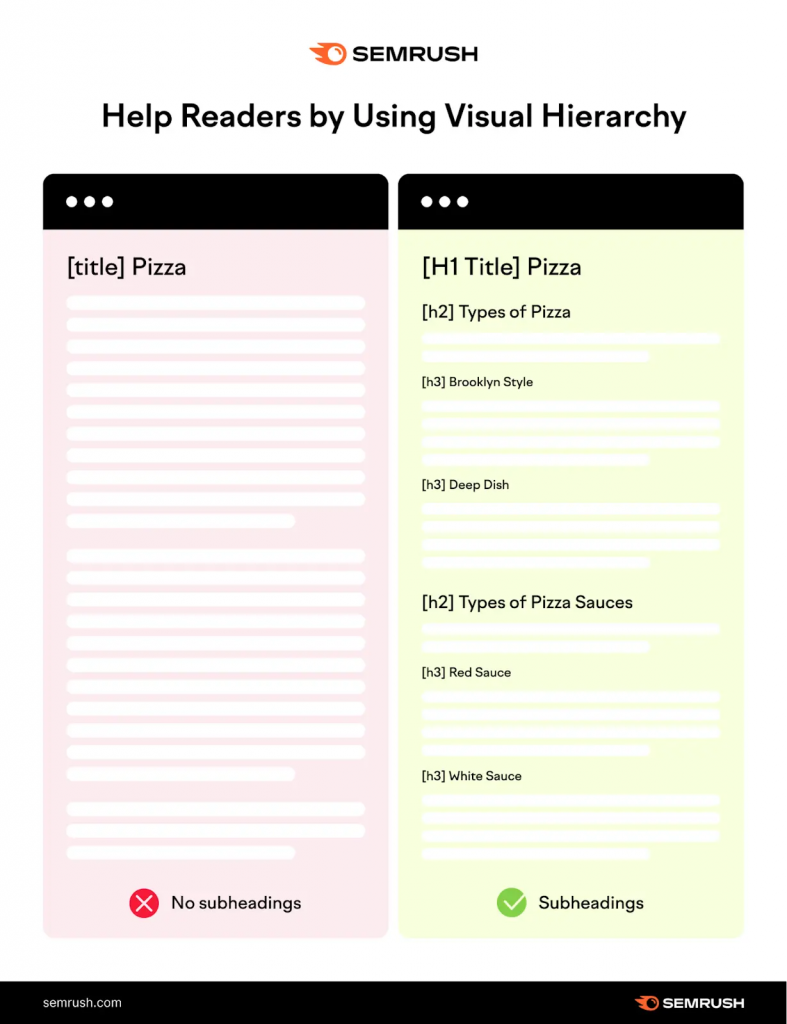
Headings are like the titles or section names on a webpage. They help organize content and make it easier for both users and search engines to understand what each part of the page is about. There are different levels of headings, and each serves a specific purpose.
Headings are usually written in larger, bold text and are structured in a hierarchy. The main title of the page is typically the H1 heading, followed by H2, H3, and so on for subheadings. Here’s how they work:
- H1 (Main Heading): This is the most important heading on the page. It tells both users and search engines what the page is about. There should only be one H1 on a page, and it typically includes the main keyword you want to rank for.
- H2 (Subheadings): These are used to break down the content into sections. They help organize your content and guide users through the page. You can have multiple H2 headings on a page, and they should relate to the main topic in the H1.
- H3 (Sub-subheadings): These are used to divide sections further. If your H2 heading talks about a broad topic, H3 headings break it down into smaller, more specific parts.
- H4, H5, H6 (Further Subdivisions): These are used for even more specific details. You don’t always need to use these unless your content is very long and complex.
Why Are Headings Important?
- User Experience: Headings help visitors navigate the page. If the headings are clear and descriptive, users can quickly find the information they need.
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization): Search engines like Google pay attention to headings because they help them understand what your content is about. Properly using headings with relevant keywords can improve your chances of ranking higher on search engine results pages (SERPs).
- Content Organization: Headings break up long text, making it easier to read. Without headings, content can seem like a big block of text, which is harder for users to digest.
How to Use Headings Effectively?
- Use One H1 per Page: The H1 should be reserved for the main topic of the page. Don’t overuse it, as it can confuse both users and search engines.
- Include Keywords: Try to include your main keywords in headings (especially H1 and H2). But avoid overstuffing them—keep it natural.
- Create a Hierarchy: Follow a logical structure. H2 should support H1, and H3 should support H2. This helps both users and search engines understand the flow of your content.
- Keep Them Descriptive and Clear: Make sure your headings tell users what the section is about. Avoid vague headings like “Introduction” or “Details” unless it’s necessary.
Example of Headings Structure
- H1: The Ultimate Guide to On-Page SEO
- H2: What is On-Page SEO?
- H3: Key Elements of On-Page SEO
- H2: Why On-Page SEO Matters
- H2: How to Optimize Your Website for On-Page SEO
- H2: What is On-Page SEO?
In this example, H1 is the main title, H2 is the sections that break down the content, and H3 provides more details about a specific part of the content.
4. Meta Description

A meta description is a short piece of text (typically 150–160 characters) that describes the content of a webpage. It appears in search engine results below the page title and URL. Although it doesn’t directly impact search rankings, it plays a crucial role in attracting users to click on your link by giving them a clear and enticing preview of what they can expect on your page.
Why Is a Meta Description Important?
- Encourages Clicks: A well-written meta description can improve your click-through rate (CTR) by enticing users to click on your link instead of others.
- Informs Users: It gives users a quick overview of the content on your page, helping them decide if your page matches their search intent.
- Highlights Keywords: When your meta description includes relevant keywords from a user’s search query, Google bolds those keywords in the search results, making your link stand out.
Best Practices for Writing Meta Descriptions:
- Be Concise: Stay within the 150–160 character limit. Longer descriptions may get cut off in search results.
- Use Action Words: Encourage users to take action with phrases like “Discover,” “Learn,” or “Find out.”
- Incorporate Keywords Naturally: Include relevant keywords that align with the page’s content but avoid keyword stuffing.
- Provide a Clear Benefit: Let users know what they’ll gain by visiting your page.
- Be Unique: Write a custom meta description for each page to avoid duplication, as duplicate descriptions can confuse search engines and users.
Example of a Meta Description:
Imagine you’re writing a meta description for a blog about “Top 10 Travel Tips.”
Title: Top 10 Travel Tips to Make Your Trips Stress-Free
Meta Description: “Plan your perfect trip with our top 10 travel tips! From packing smart to finding cheap flights, discover how to make your travels stress-free and enjoyable.”
Here’s how this works:
- Length: The meta description is under 160 characters, ensuring it displays fully in search results.
- Keywords: It includes important keywords like “travel tips,” “packing smart,” and “stress-free,” which users might be searching for.
- Enticing: It’s written in a way that makes users curious and provides value, increasing the chances they’ll click.
5. Content
In the world of SEO (Search Engine Optimization), content refers to any information, text, or media on a website that provides value to its audience. Content is the backbone of SEO because it directly connects search engine algorithms with what users are searching for. Simply put, SEO content is designed to attract, engage, and satisfy the needs of both users and search engines.
Why is Content Important for SEO?
Content serves multiple roles in SEO, such as:
- Relevance: Search engines like Google analyze your content to determine if it’s relevant to the user’s query.
- Authority: High-quality, well-researched content builds authority, which helps improve rankings over time.
- Engagement: Engaging content keeps users on your website longer, reducing bounce rates and signaling to search engines that your page provides value.
- Keywords: Content allows you to strategically place keywords, which help search engines understand what your page is about.
Types of SEO Content
- Blog Posts:
- These are detailed articles on specific topics designed to provide value, answer questions, or entertain.
- Example: A blog titled “10 Tips to Save Electricity at Home.”
- Product Pages:
- Found on e-commerce sites, these describe the features and benefits of a product.
- Example: A page describing the features of “Energy-Efficient LED Bulbs.”
- Landing Pages:
- These are designed for marketing campaigns or specific goals like lead generation.
- Example: A landing page for “Free SEO Consultation.”
- How-To Guides:
- Step-by-step tutorials that educate the audience.
- Example: “How to Install a Circuit Breaker Safely.”
- Videos:
- Explainer videos or tutorials enhance user engagement and can also rank in search engines (YouTube is a search engine too!).
- Example: A video showing “How to Replace a Thermostat.”
- Infographics:
- Visual content that presents data or processes in an easy-to-digest format.
- Example: An infographic titled “The Evolution of Renewable Energy.”
- Listicles:
- These are list-based articles, which are easy to read and share.
- Example: “Top 10 SEO Tools for Beginners.”
- Case Studies:
- Detailed descriptions of how a solution or product benefited a client.
- Example: “How XYZ Company Increased Traffic by 200% Using On-Page SEO.”
- FAQs:
- Pages that answer commonly asked questions.
- Example: “What Is a Meta Description? And Why Is It Important?”
Characteristics of Good SEO Content
To rank well in search engines and satisfy user intent, SEO content should have the following characteristics:
- Relevant to User Intent:
- Ensure your content matches what users are searching for. If someone searches “How to bake a cake,” your content should focus on steps and ingredients rather than the history of baking.
- High-Quality and Well-Researched:
- Content should be accurate, valuable, and insightful. Avoid fluff.
- Original:
- Search engines penalize duplicate content. Always create unique content for your website.
- Keyword Optimized:
- Use target keywords naturally throughout the content, including in the title, headers, and body. Avoid keyword stuffing.
- Engaging and Readable:
- Write in a conversational tone, use short sentences, and break the text into smaller sections with headers.
- Multimedia Elements:
- Include images, videos, charts, or infographics to make the content visually appealing and engaging.
- Optimized for Mobile:
- Ensure your content looks good and is easy to read on smartphones and tablets.
6. Schema Markup
Schema Markup is a form of code that helps search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo better understand your website’s content. It is written in a structured format, such as JSON-LD, and added to your website’s HTML. This extra layer of information makes it easier for search engines to interpret your content and present it in a more useful way in search results.
Think of Schema Markup as a translator between your website and search engines. While humans can look at a page and understand its purpose, search engines need extra help to figure out specific details, such as a product’s price, a business’s address, or an event’s date.
Why is Schema Markup Important?
Schema Markup helps enhance your website’s visibility in search results by creating rich snippets. Rich snippets are the additional information that appears below the main link on a search engine results page (SERP). For example:
- For a recipe: It might show cooking time, ingredients, and ratings.
- For an event: It can display the event date, time, and location.
- For a business: It could highlight the address, phone number, and customer reviews.
These extra details make your website stand out, improving the chances of users clicking on your link.
Types of Schema Markup
There are various types of Schema Markup that cater to different kinds of content. Some of the most common ones include:
- Article Schema: Used for news articles or blog posts.
- Product Schema: Helps showcase product details like price, availability, and ratings.
- Event Schema: Displays event dates, locations, and ticket availability.
- FAQ Schema: Organizes and highlights frequently asked questions.
- Review Schema: Adds star ratings and review details.
How Does Schema Markup Work?
When you add Schema Markup to your website, search engines use it to understand the structure of your content better. For example, if you have a recipe page, Schema Markup can define the title, cooking time, ingredients, and instructions in a way that search engines can process easily.
Search engines then use this data to display your page in an enhanced format, helping users get a quick overview of your content before they even click the link.
Benefits of Schema Markup
- Improved Click-Through Rates (CTR): Rich snippets catch users’ attention and encourage clicks.
- Better Search Rankings: While not a direct ranking factor, Schema Markup helps search engines understand your site better, indirectly improving SEO performance.
- Increased User Engagement: Clear, detailed search results improve the user experience.
- Competitive Edge: Rich snippets make your website stand out from others on the SERP.
- Supports Voice Search: Schema Markup provides structured data that voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant can use to answer user queries accurately. As Google expands AI Overviews, clear structure and disambiguation help your content be summarized faithfully and surfaced alongside concise answers. What is AI Overview?
- Enhances Local SEO: Adding local business Schema can help your business appear in location-specific searches, making it easier for customers to find you.
- Boosts Brand Trust: Rich snippets like ratings, reviews, and business details make your website look more professional and trustworthy to users.
How to Add Schema Markup to Your Website?
Adding Schema Markup can be done in several ways:
- Manual Code Addition: Write JSON-LD code and insert it into your website’s HTML.
- Using Plugins: Platforms like WordPress offer plugins (e.g., Rank Math, Yoast) that generate Schema Markup automatically.
- Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper: A free tool by Google that helps generate Schema code for your website.
Once added, you can test your Schema Markup using Google’s Rich Results Test Tool to ensure everything is working correctly.
7. Alt Tag
An Alt tag (short for “alternative text”) is a piece of code used in HTML to describe the content of an image on a webpage. It provides a text-based description that explains what the image is about. This tag is written inside the HTML code for an image and is essential for both website accessibility and search engine optimization (SEO).
Why Are Alt Tags Important?
Alt tags play a critical role in improving user experience and website performance for the following reasons:
1. Accessibility
- Alt tags help visually impaired users understand the content of an image through screen readers, which read out the description.
- This ensures your website is more inclusive and meets accessibility standards like WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines).
2. SEO Benefits
- Search engines, like Google, cannot “see” images, but they can read Alt tags. A clear, descriptive Alt tag helps search engines understand what the image is about.
- Proper use of Alt tags can improve your website’s ranking in image search results.
3. Backup for Broken Images
- If an image fails to load, the Alt text is displayed in its place, giving users an idea of what the image was supposed to show.
How to Write a Good Alt Tag?
Here are some tips for writing effective Alt tags:
- Be Descriptive
- Clearly describe the image content. For example:
- ✅ Good: “Red apple on a wooden table.”
- ❌ Bad: “Apple.”
- Clearly describe the image content. For example:
- Use Keywords Naturally
- Include relevant keywords, but avoid keyword stuffing. For example:
- ✅ Good: “Energy-efficient LED light bulb for home lighting.”
- ❌ Bad: “Light bulb, LED light bulb, energy-efficient bulb, home bulb.”
- Include relevant keywords, but avoid keyword stuffing. For example:
- Keep It Concise
- Alt tags should be brief and to the point—generally 125 characters or fewer.
- Avoid Words Like ‘Image of’ or ‘Picture of’
- Screen readers already identify the content as an image, so there’s no need to repeat this.

8. Urls/Slugs
A Page URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the unique address that points to a specific webpage on the internet. Just like your home address tells people where to find you, a Page URL tells web browsers and search engines where to locate a webpage. It serves as a key component of the web, enabling users to visit websites, access information, and share links with others.
Understanding the Structure of a Page URL
A typical Page URL consists of several parts:
- Protocol:
The protocol tells the browser how to communicate with the server. Common examples are:- HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol)
- HTTPS (Secure version of HTTP, with encryption for added security)
Example: https://
- Domain Name:
This is the name of the website or the server hosting the webpage.
Example: www.example.com - Path:
The path specifies the exact page or location within the website. It comes after the domain name and is often structured in folders or directories.
Example: /blog/what-is-page-url - Parameters (Optional):
Some URLs include parameters that pass additional data, such as search queries or session IDs. These usually follow a ? in the URL.
Example: ?search=page+url - Fragment (Optional):
A fragment is a section of the page, indicated by a #. It directs the user to a specific part of the webpage.
Example: #examples
Why Are Page URLs Important?
- User Navigation:
URLs guide users to the exact location of the content they’re looking for on a website. - Search Engine Optimization (SEO):
Search engines use URLs to understand the structure and content of a website. A clear, descriptive URL improves a page’s visibility in search results. - Link Sharing:
URLs make it easy to share specific pages or resources with others via email, social media, or messaging. - Website Organization:
A logical URL structure helps keep websites organized and makes it easier to manage content.
Best Practices for Page URLs
- Keep It Simple and Descriptive:
A good URL should give users and search engines a clear idea of the page content.
Example: https://www.example.com/blog/page-url-guide - Avoid Special Characters:
Use only letters, numbers, and hyphens in URLs. Avoid spaces, underscores, or symbols like %. - Use Keywords:
Incorporate relevant keywords naturally to help improve SEO rankings. - Maintain Consistency:
Follow a logical structure across the website for better user experience.
Example:- /blog
- /blog/what-is-page-url
- Use HTTPS:
Always opt for HTTPS over HTTP to provide a secure connection and improve trustworthiness.
Examples of Good and Bad Page URLs
- Good URL:
https://www.example.com/products/electrical-switches - Bad URL:
https://www.example.com/page?id=12345
9. Internal Linking
Internal linking is a process where you connect one page of your website to another page on the same website using hyperlinks. These links allow users to navigate through your site and help search engines understand the structure and hierarchy of your content.
For example, if you have a blog about SEO, you might link from a page about “On-Page SEO” to another page discussing “Keyword Research.” This is an internal link because both pages belong to the same website.
Why is Internal Linking Important?
Internal linking serves multiple purposes, including:
1. Improved User Navigation
When you provide relevant internal links, users can easily find more information on related topics. This enhances their experience and keeps them on your site longer.
2. Boosts SEO
Search engines, like Google, use internal links to discover and index pages on your site. When your pages are properly linked, it signals that your website is well-structured and organized.
3. Distributes Link Equity
Internal links help pass “link equity” (or link juice) from one page to another. Pages with more internal links often receive higher importance in the eyes of search engines, which can improve their rankings.
4. Encourages Engagement
Internal links can guide visitors to high-value pages, such as product pages or other helpful articles. This increases engagement and can lead to more conversions.
Best Practices for Internal Linking
To get the most out of internal linking, follow these tips:
1. Use Descriptive Anchor Text
Anchor text is the clickable part of a hyperlink. Use text that clearly describes the linked page’s content. For example, instead of “click here,” write “learn more about keyword research.”
2. Link to Relevant Pages
Always link to pages that add value to the user. Irrelevant links can frustrate users and harm your SEO.
3. Avoid Overlinking
Don’t stuff too many internal links on a single page—it can confuse users and dilute the value of the links.
4. Prioritize Important Pages
Ensure your most important pages, like product or service pages, receive more internal links. This tells search engines these pages are key to your site.
5. Fix Broken Links
Always check for broken internal links and fix them. Broken links disrupt user experience and can negatively affect your site’s SEO.
10. Mobile Responsiveness
Mobile responsiveness refers to a website’s ability to adjust and display properly on devices of various screen sizes, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, and desktops. A mobile-responsive website ensures that users have a seamless and easy experience, regardless of the device they use to access it.
Key Features of Mobile Responsiveness:
- Adaptive Layouts: A responsive website automatically adjusts its layout to fit the screen size. For example, the content on a smartphone will stack vertically for easy scrolling, while on a larger screen, it might display side by side.
- Readable Text: Mobile-responsive websites make sure text is legible without the need for zooming or horizontal scrolling.
- Optimized Images: Images resize automatically to fit the screen without distorting or slowing down page load times.
- Clickable Buttons and Links: The website’s buttons, links, and interactive elements are designed to be easily clickable on smaller screens without accidentally tapping the wrong option.
- Fast Loading Times: Responsiveness often goes hand-in-hand with optimizing a website’s loading speed, ensuring quick access even on slower mobile networks.
Why is Mobile Responsiveness Important?
- Improved User Experience: A responsive design provides a smooth and enjoyable experience for users, making them more likely to stay on your website and interact with your content.
- Higher Search Engine Rankings: Google and other search engines prioritize mobile-responsive websites in search results. This means a responsive site can help improve your visibility online.
- Increased Reach: With more people using smartphones to browse the internet, a mobile-responsive site ensures you don’t lose potential visitors or customers.
- Better Conversion Rates: When users can easily navigate and interact with your site on their mobile devices, they’re more likely to take desired actions, like making a purchase or filling out a form.
- Cost-Effective Maintenance: Instead of creating separate websites for desktop and mobile users, a single responsive site saves time and resources in the long run.
How to Check if a Website is Mobile-Responsive?
- Resize Your Browser Window: On a desktop, shrink your browser window to see if the layout adjusts dynamically.
- Use Online Tools: Tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test can analyze and confirm a website’s mobile responsiveness.
- Test on Multiple Devices: Open the website on a smartphone, tablet, and desktop to observe how it looks and functions.
How to Make a Website Mobile-Responsive?
- Use Responsive Web Design (RWD): Implement flexible grids, images, and CSS media queries to make the website adaptable.
- Choose a Mobile-Friendly Theme: Many modern website builders, like WordPress, offer themes specifically designed for responsiveness.
- Optimize Images and Media: Use formats and sizes that load quickly without sacrificing quality.
- Test Regularly: Continuously test your website on various devices to ensure it remains responsive after updates.

How to Check a Competitor’s On-Page SEO?
Understanding your competitors’ on-page SEO strategy can give you valuable insights into improving your website’s performance. Here’s a step-by-step guide to checking a competitor’s on-page SEO effectively:
1. Analyze Their URLs
- Look at the structure of their URLs.
- Good URLs are short, descriptive, and include the primary keyword.
- Example: Instead of www.example.com/page123, it should look like www.example.com/best-smartphones.
2. Check Their Page Titles
- Review the titles of their web pages.
- Effective page titles are:
- Under 60 characters.
- Keyword-rich and specific.
- Engaging enough to attract clicks.
- Example: “Top 10 Smartphones of 2024 – Expert Reviews & Buyer’s Guide.”
3. Review Meta Descriptions
- Meta descriptions provide a summary of the page content.
- Check if your competitor uses compelling, keyword-optimized meta descriptions within 150-160 characters.
- These descriptions should encourage users to click.
4. Inspect Their Headings (H1, H2, H3)
- Headings help organize content and improve readability.
- Check if your competitor uses:
- An H1 tag with the primary keyword.
- Subheadings (H2, H3) for clear structure and additional keywords.
5. Evaluate Their Content
- Review the quality and length of their content:
- Is the content well-written and informative?
- Does it include keywords naturally?
- Are there engaging visuals (images, videos, or infographics)?
- Compare the word count and depth of their content to yours.
6. Inspect Internal Linking
- Check how they link to other pages within their website.
- A good internal linking strategy helps users navigate and distributes SEO value across the site.
- Example: If their blog post discusses a product, it might link to the product page.
7. Analyze External Linking
- Review the outbound links they use.
- Competitors often link to high-authority websites to add credibility to their content.
- Ensure they don’t link to low-quality or spammy sites.
8. Look at Their Keyword Usage
- Examine how they use keywords across their page:
- In the title, URL, and headings.
- Naturally in the content, avoiding keyword stuffing.
- In image alt text and descriptions.
9. Check for Multimedia Optimization
- Ensure they optimize images, videos, and other media:
- Images should have descriptive file names (e.g., blue-widget.jpg instead of IMG123.jpg).
- Alt text should include keywords where relevant.
- Videos should have captions and descriptions.
10. Examine Mobile-Friendliness
- Visit their site on a mobile device.
- Check if the layout adjusts smoothly and remains user-friendly.
- Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test can also be used.
11. Review Page Speed
- Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to analyze their page loading time.
- Slow-loading pages can affect rankings and user experience.
12. Check Schema Markup
- Look for structured data (schema) on their site.
- Schema enhances search engine results with rich snippets, such as ratings, FAQs, and events.
13. Inspect Their Call-to-Action (CTA)
- Note how they guide users with CTAs like “Buy Now,” “Learn More,” or “Sign Up.”
- Their CTAs should be visible, engaging, and aligned with the page’s intent.
14. Assess Social Media Integration
- Check if they include social sharing buttons on their pages.
- This encourages users to share the content, driving more traffic.




